When it comes to rechargeable batteries, it can be difficult to understand the vast amount of technical terms used to explain the different functionalities and capabilities.
If you’re baffled by battery language, have no fear! We’ve put together a battery encyclopedia for your with the most frequent terms you may see when battery shopping, so you don’t have to guess again.

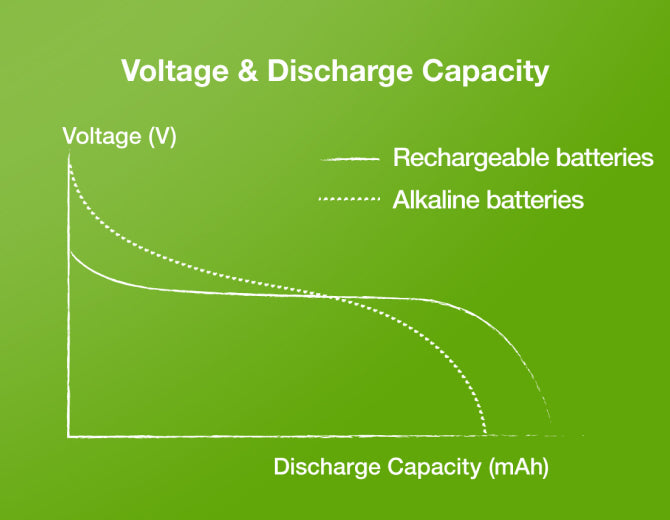
What Does Voltage Mean?
Probably the most commonly understood battery technical term, voltage (V) refers to the difference in electric potential between the positive and negative terminal of a battery. Depending on the size and chemistry of the battery, the voltage can vary significantly (1.5V for common alkaline batteries such as AA, AAA cells, 3V for small lithium coins or 9V for 9V batteries).
When picking out the right battery, voltage is also crucial to consider. That’s because some devices will not operate properly (or will only operate for a short time) if paired with less-than-ideal voltage. Here’s something to remember: While alkaline batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, rechargeable batteries have 1.2 volts; on the other hand, an alkaline battery will start its initial charge at 1.5 volts before tapering down to 1.2 volts in later charges. However, rechargeable batteries maintain their voltage for a longer time, whereas the non rechargeable counterparts steadily lose their voltage.
What is mAh Capacity?
Battery capacity is measured in mAh (milliampere/hour) and refers to the maximum potential amount of energy delivered by the battery in a single discharge. When looking at rechargeable batteries, you may see the capacity indicated as XXX mAh, which is found through the following calculation: discharge (milliampere) x discharging time (hour).
Generally, higher capacity ratings for the same battery type result in longer run time. However, the battery performance will vary according to the battery age, temperature and the type of electronic device in use. Powering high drain electronic appliances like professional cameras, gaming controllers or remote controlled cars will require higher power compared to a clock. Therefore, it is advisable to go for batteries with higher capacities designed for your device to enjoy the best battery performance.
What Does Cycle Life Mean?
The cycle life of a battery refers to the number of complete charge-discharge cycles that a battery is able to support before its capacity and performance visibly reduce. For example, GP ReCyko Pro batteries have a massive cycle life of up to 1,500 times!
Cycle life can be affected by two key factors: time and the number of cycles completed. One of the best ways to maintain your rechargeable batteries’ lifespan is to ensure that the battery is not subject to adverse conditions such as extreme temperature, deep cycling and excessive over charge/over discharge. In addition, make sure to store batteries in a cool, dry place, or ventilated at room temperature and away from direct sunlight.
What Does Shelf Life Mean?
When it comes to rechargeable batteries, shelf life refers to the amount of time a battery can sit idle without becoming unusable. All batteries self-discharge during storage, but to a different extent. However, proper storage can slow this process. Much like cycle life, to maintain good battery performance it is recommended to keep the batteries in a cool and dry place. In addition, for first-time usage or after long term storage, we recommend fully charging the battery before use.
What is Battery Self-Discharge?
When batteries are not in use, they still expend their energy through internal chemical reactions. Because of this, a phenomenon known as self-discharge occurs, where idle batteries reduce the stored charge in the battery and gradually decrease the capacity of the battery.
Unfortunately, battery self-discharge cannot be entirely avoided, but depending on the battery, the rate at which this self-discharge occurs can vary. For example, GP ReCyko AAA Rechargeable Battery can stay up to 80% charged after 12 months due to a low self-discharge rate.
What is the Battery Memory Effect?
The memory effect can occur when a battery is repeatedly charged before all of its stored energy is depleted. This leads to the battery ‘memorising’ the decreased charging cycle and significantly shortening the potential operating time. This effect could be reversed with proper battery care, such as completely discharging a battery by leaving it in a device and then fully recharging the battery. However, today with the latest generations of NiMH rechargeable batteries this is no longer an issue.
Discover our wide assortment of rechargeable batteries
Let’s Stay in Touch!
Sign up to our newsletter to get the latest blogs, news and special offers. You can unsubscribe at any time.








